Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol used to prevent loops in the network by creating a logical topology of the network. It is used in Cisco IOS devices such as switches and routers to ensure redundant links are not creating broadcast storms and loops. STP works by assigning each switch or router port a role, either root bridge, designated bridge, non-designated bridge or alternate port. The root bridge is the most important component as it determines which ports are blocked and which are forwarding traffic.
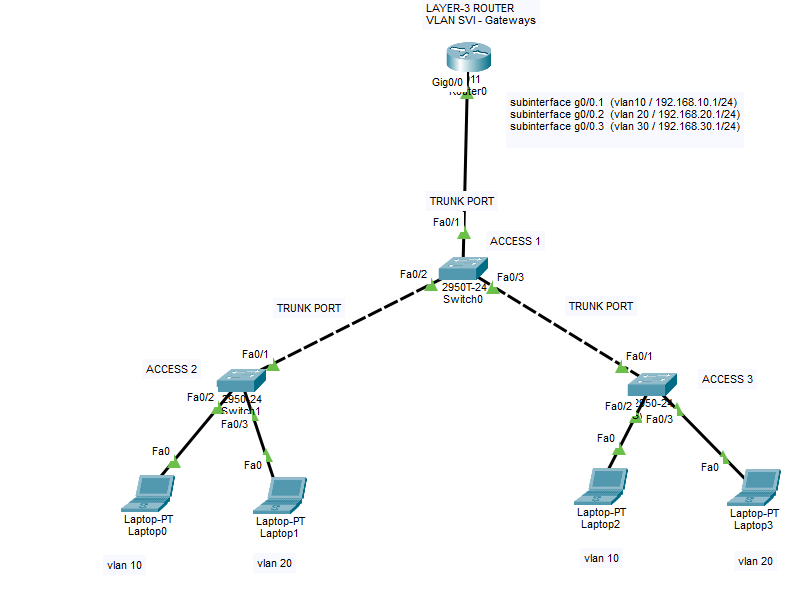
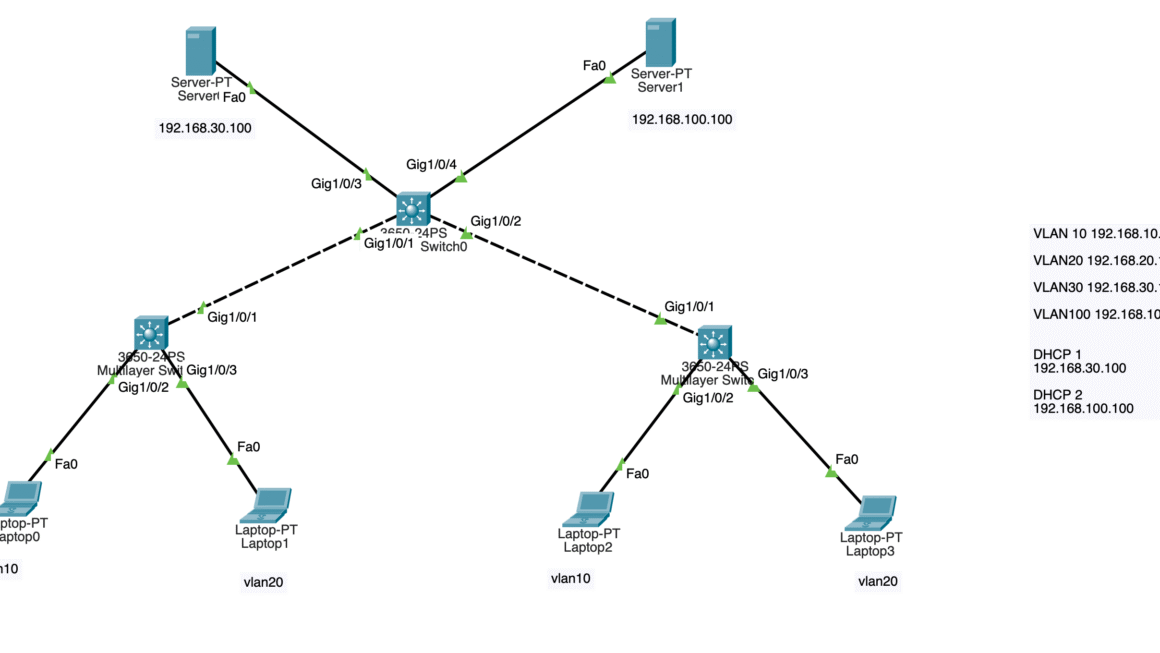
There are two different STP modes: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP). RSTP is used when there is one VLAN per switch while MSTP is used when there are multiple VLANs per switch. To implement STP on multiple switches or routers, you need to configure each device with the same STP mode and set up Routing Information Protocol (RIP) between them so
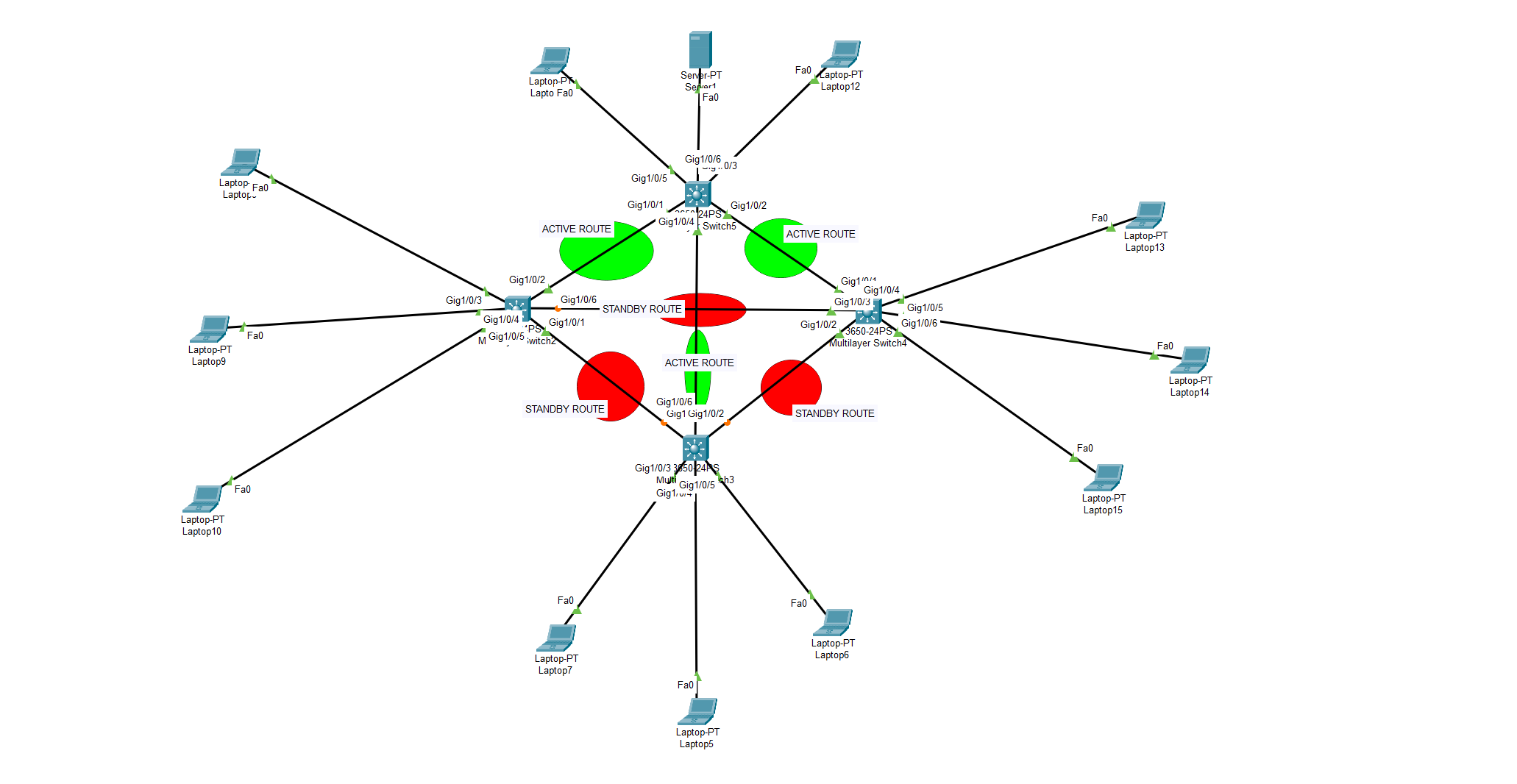
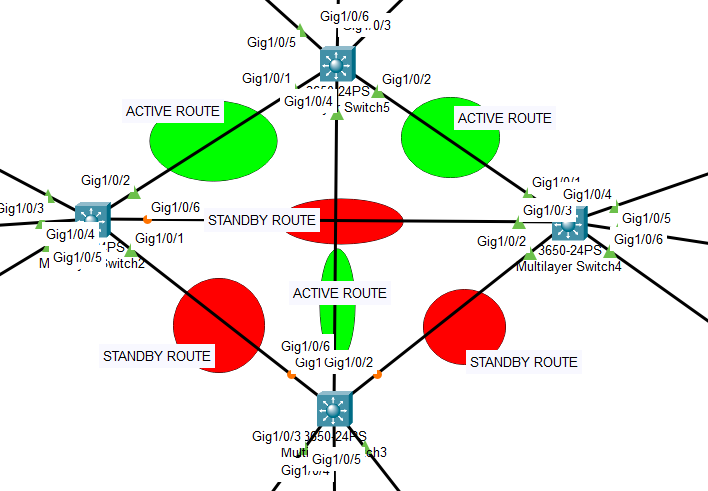
In this example, we used STP protocol feautres as “high availability route” implementation. STP enabled switches can understand the root route and spare other alternative routes as backup.
Switch#show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0009.7CB8.8D11
Cost 4
Port 2(GigabitEthernet1/0/2)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 00D0.97AD.BE67
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 20
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi1/0/1 Desg FWD 4 128.1 P2p
Gi1/0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.4 P2p
Gi1/0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
Gi1/0/6 Altn BLK 4 128.6 P2p
Gi1/0/2 Root FWD 4 128.2 P2p
Gi1/0/5 Desg FWD 19 128.5 P2p
Switch#The spanning tree algorithm functions in two following ways:
- Loop-free topology, called a spanning tree, via an automated process. The topology is dynamically pruned to the spanning tree by declaring certain redundant ports on a switch and placing them into a “blocking” state.
- If possible, automatically recovering from a switch failure that could result in the partitioning of the extended LAN by reconfiguring the spanning tree to use redundant paths.
By default, RSTP is the mode enabled on every port of a switch. It prevents Layer 2 loops in a network.
MOST USEFUL FEATURE of STP protocol is that, it prevents unwanted looping from end-user’s side.
STP MODES
Classic STP—Provides a single path between any two end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops.
Rapid STP (RSTP)—Detects network topologies to provide faster convergence of the spanning tree. …
Multiple STP (MSTP)—MSTP is based on RSTP.